What to Do in Case of a Camping Emergency?
Camping is a cherished activity that offers a break from the hustle and bustle of daily life, providing an opportunity to reconnect with nature. However, the wilderness, with its unpredictable conditions, can present various challenges and emergencies. Preparing for these contingencies is crucial for ensuring a safe and enjoyable camping experience. This comprehensive guide explores essential steps to take during a camping emergency, ensuring that you are well-equipped to handle any situation that may arise.
Camping Emergencies
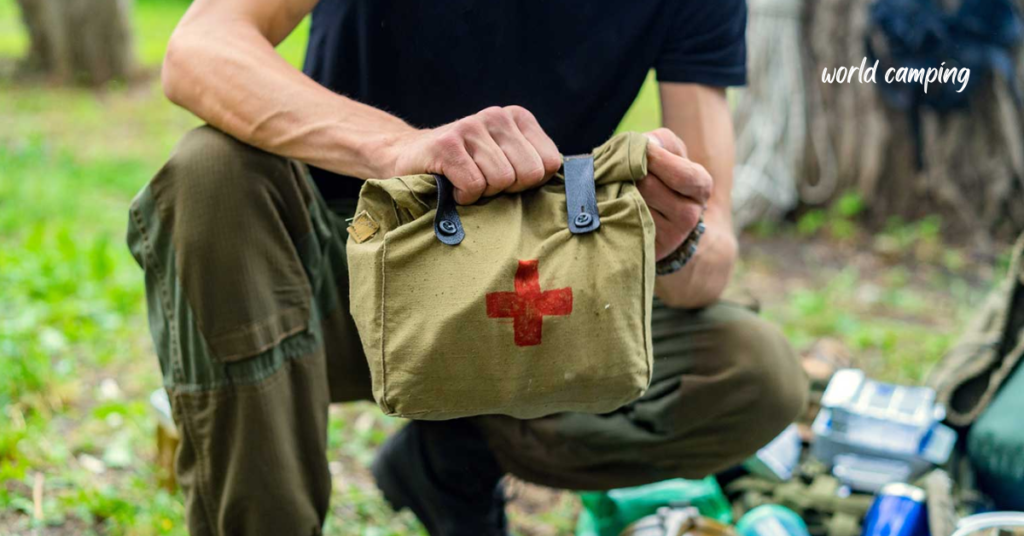

Camping emergencies encompass a spectrum of unforeseen situations that can jeopardize the safety and well-being of outdoor enthusiasts. From minor mishaps to life-threatening scenarios, these emergencies demand preparedness and quick, effective responses. Among the most common camping emergencies are medical situations, where injuries, allergic reactions, or sudden illnesses can occur unexpectedly. It’s essential for campers to have basic first aid knowledge and carry a well-equipped medical kit to address such incidents promptly and effectively.
Importance of Preparedness
Preparedness is not just a precautionary measure; it’s a lifeline in the unpredictable realm of outdoor adventures. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it can make all the difference between a minor inconvenience and a life-threatening ordeal. Understanding potential emergencies and being equipped with the knowledge and resources to respond effectively can significantly enhance safety and peace of mind for campers.
At the core of preparedness lies the paramount concern for safety. Whether it’s ensuring everyone knows basic first aid procedures or packing essential survival gear, the ultimate aim is to safeguard the well-being of all individuals venturing into the wilderness. By anticipating potential risks and taking proactive measures to address them, campers can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents or injuries.
Preparedness plays a crucial role in minimizing panic during emergencies. When campers are equipped with the necessary skills and resources to handle unforeseen situations, they are less likely to succumb to fear or anxiety. Instead, they can approach challenges with a clear mind and a sense of confidence, which is vital for making sound decisions and executing effective emergency responses.
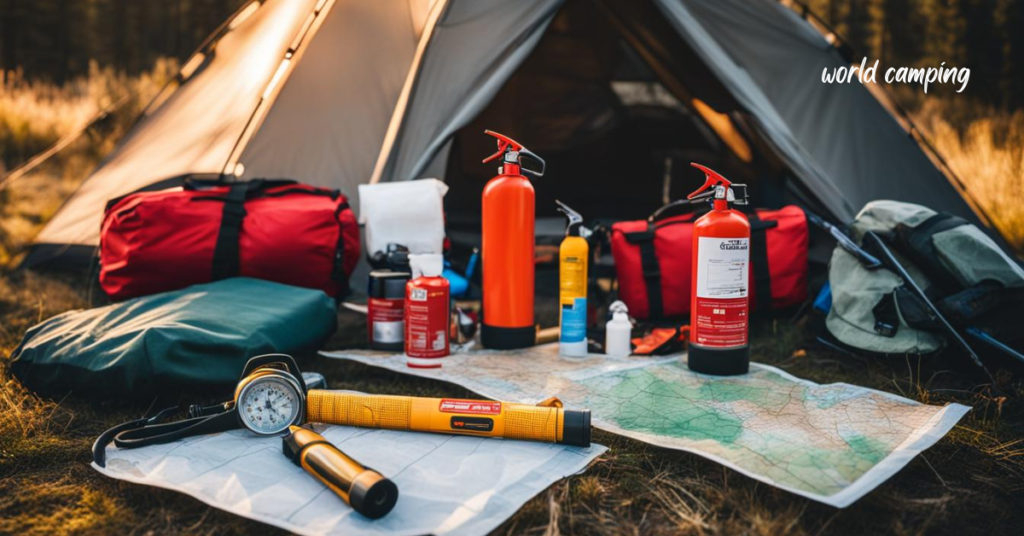
Essential Gear

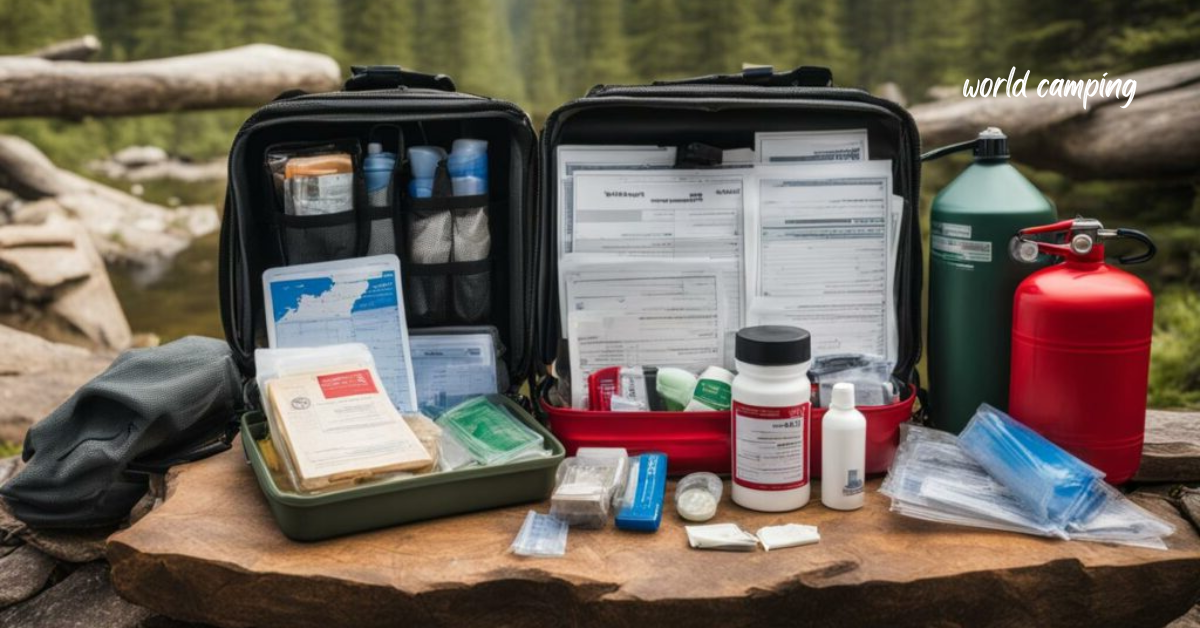
A well-stocked first aid kit is a cornerstone of outdoor safety. It should contain a comprehensive array of supplies, including bandages, antiseptics, pain relievers, and any necessary medications for specific medical conditions. Whether treating minor cuts and scrapes or managing more serious injuries, a first aid kit equips campers with the resources to address medical emergencies promptly and effectively.
Navigation tools are indispensable for wilderness exploration. Maps, compasses, and GPS devices provide vital guidance, helping campers navigate unfamiliar terrain and avoid getting lost. By plotting routes, identifying landmarks, and staying oriented to their surroundings, outdoor enthusiasts can mitigate the risk of becoming disoriented and ensure they reach their destination safely.
Emergency supplies are essential for preparing for unexpected situations. A multi-tool offers versatility, providing various functions such as cutting, screwdriving, and bottle opening in a compact package. A reliable flashlight with extra batteries ensures visibility during low-light conditions or emergencies at night. A whistle can serve as a powerful signaling device, alerting others to your presence in case of emergencies. Additionally, emergency blankets provide warmth and insulation, crucial for surviving exposure to cold or inclement weather.
Communication devices are indispensable for staying connected and summoning help when needed. Mobile phones, satellite phones, or two-way radios enable campers to reach out for assistance in case of emergencies or unexpected situations. Maintaining communication with emergency services or fellow campers enhances safety and facilitates prompt responses to any crises that may arise.
Handling Medical Emergencies in the Wilderness
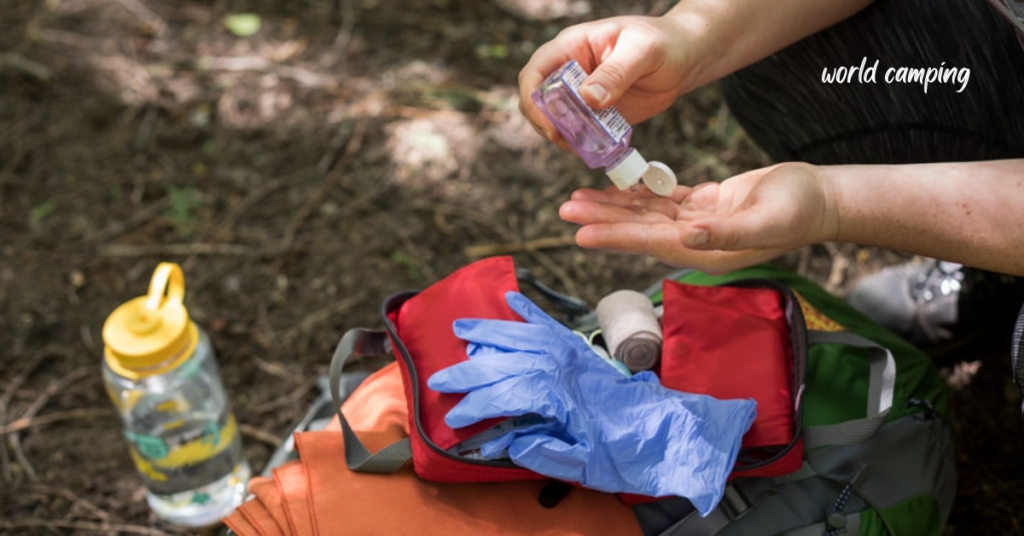

Medical emergencies are among the most common issues encountered while camping. From minor injuries to serious health crises, knowing how to respond appropriately can make a significant difference.
Immediate Response to Medical Emergencies
When faced with a medical emergency in a camping or outdoor setting, knowing how to respond swiftly and effectively can be a lifesaver. The immediate response to such situations can make all the difference in ensuring the best possible outcome for the injured individual.
The first step is to carefully evaluate the circumstances surrounding the medical emergency. Ensure the area is safe for you to approach the injured person, taking note of any potential hazards such as uneven terrain or nearby wildlife. Next, assess the nature and severity of the injury or illness. Determine if the person is conscious, breathing, and if there are any visible wounds or signs of distress.
Time is of the essence in a medical emergency, so it’s crucial to summon professional assistance as quickly as possible. If you have access to a mobile phone with service, dial emergency services immediately and provide them with essential details about the situation, including your location and the condition of the injured person. In areas with no mobile service, utilize alternative methods such as a whistle or signaling device to alert nearby campers or park rangers, who can then relay the emergency to authorities.
Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke
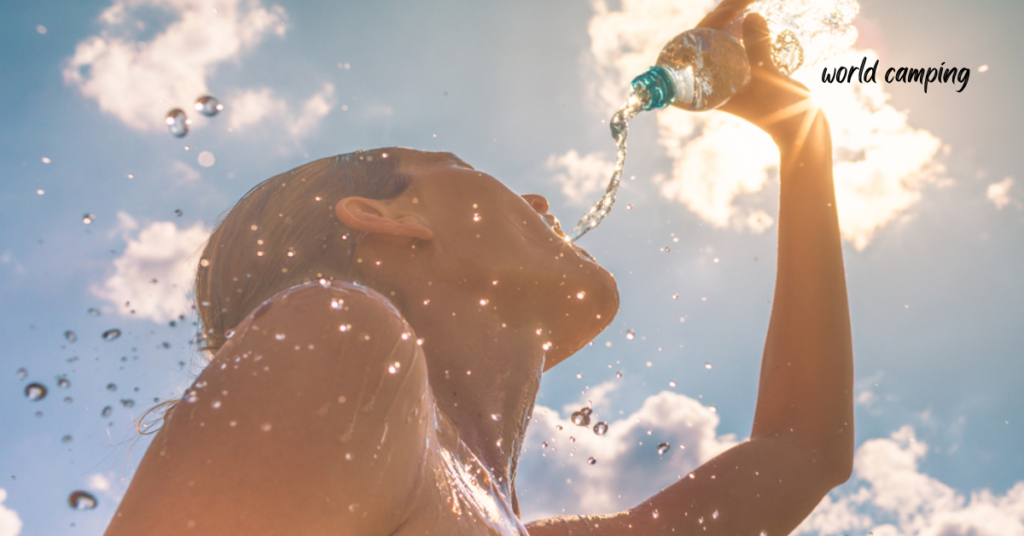

Heat exhaustion and heat stroke are serious conditions that can occur when the body overheats, often as a result of prolonged exposure to high temperatures or strenuous physical activity in hot environments. Recognizing the symptoms and taking prompt action is crucial in preventing these conditions from escalating into life-threatening emergencies.
The first step in treating heat-related illnesses is to move the affected person to a shaded or cool area away from direct sunlight. This helps reduce their exposure to heat and allows their body to begin cooling down naturally. If indoors, turn on fans or air conditioning to further aid in lowering the ambient temperature.
Dehydration often accompanies heat-related illnesses, so it’s important to rehydrate the individual promptly. Offer water or electrolyte drinks to replenish fluids and restore electrolyte balance. Encourage them to drink slowly and steadily to avoid overwhelming their system.
Lowering the body temperature is essential in treating heat exhaustion and preventing heat stroke. Use cool cloths or towels to apply to the skin, focusing on areas with high blood flow such as the neck, wrists, and groin. Alternatively, use fans or misting devices to facilitate evaporative cooling. In severe cases of heat stroke, where the person’s temperature is dangerously high and they are at risk of organ damage, it may be necessary to immerse them in cool water or apply ice packs to rapidly lower their body temperature.
Dealing with Weather-Related Emergencies
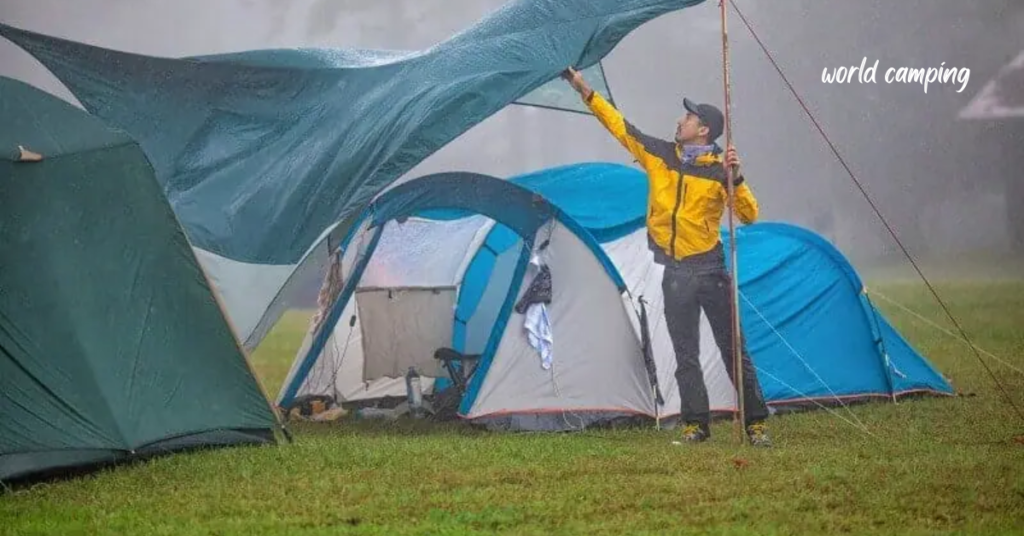

Weather-related emergencies are one of the most unpredictable and potentially dangerous situations campers can face. Weather conditions can change rapidly, turning a peaceful camping trip into a hazardous ordeal. This section delves into the various types of weather-related emergencies, how to prepare for them, and the appropriate actions to take when they occur.
Understanding Weather Hazards
Understanding weather hazards is paramount for anyone spending time outdoors, as weather conditions can change rapidly and pose significant risks to safety. From sudden thunderstorms to extreme temperatures, being able to recognize the signs of impending weather hazards is essential for taking timely action to mitigate risks and ensure the well-being of individuals.
Extreme temperatures, whether excessively hot or cold, can pose serious health risks to individuals exposed to them for prolonged periods. Recognizing the signs of heat exhaustion, such as excessive sweating, weakness, and nausea, is essential in hot climates. Conversely, in cold environments, symptoms of hypothermia, including shivering, confusion, and loss of coordination, should prompt immediate action to warm the affected person and prevent further heat loss.
High winds can create hazardous conditions by causing objects to become projectiles, toppling trees, and damaging structures. Being aware of weather forecasts indicating strong winds and recognizing signs such as swaying trees or blowing debris can help individuals take precautions to secure loose items, seek shelter in sturdy structures, and avoid outdoor activities that may put them at risk of injury.
Flash floods can occur suddenly, especially in areas with steep terrain or poor drainage, posing a significant threat to individuals in low-lying areas or near waterways. Understanding the potential for flash flooding based on weather conditions, such as heavy rainfall or rapid snowmelt, is crucial for avoiding areas prone to flooding and seeking higher ground if necessary.
Thunderstorms and Lightning
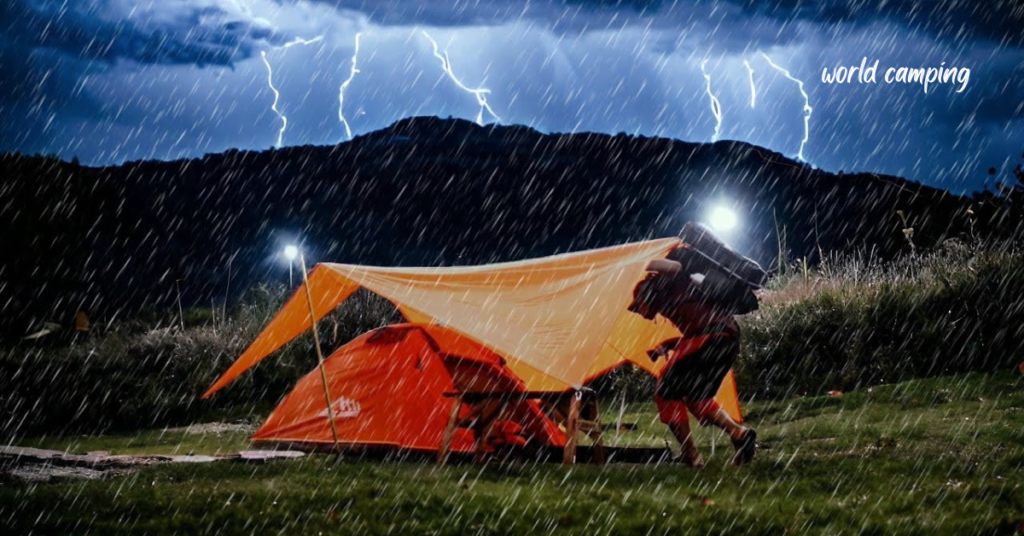

Understanding the risks associated with thunderstorms and lightning is crucial for outdoor safety, as these weather phenomena can pose significant dangers to individuals exposed to them. Thunderstorms can develop rapidly, bringing heavy rain, strong winds, and lightning strikes that can occur even when the storm seems distant.
Early detection of thunderstorm activity is key to staying safe outdoors. Keep an eye out for darkening skies, a sudden drop in temperature, increasing wind speed, and distant rumbling thunder. These signs indicate the approach of a thunderstorm and should prompt immediate action to seek shelter and avoid exposure to lightning.
When you notice the early signs of a thunderstorm, it’s essential to seek shelter promptly. If you’re outdoors, find a sturdy building or a hard-topped vehicle where you can take refuge from the storm. Avoid seeking shelter under trees or near tall objects that may attract lightning strikes. If you’re camping and don’t have access to a building or vehicle, seek out low-lying areas away from tall trees and set up camp away from potential hazards.
Lightning is attracted to tall structures, trees, and metal objects, making them dangerous places to be during a thunderstorm. Stay away from isolated trees, telephone poles, towers, and other tall objects that may increase your risk of being struck by lightning. If you’re caught outdoors with no shelter available, crouch low to the ground with your feet close together, minimizing contact with the ground and reducing the risk of a direct lightning strike.
Managing Wildlife Encounters
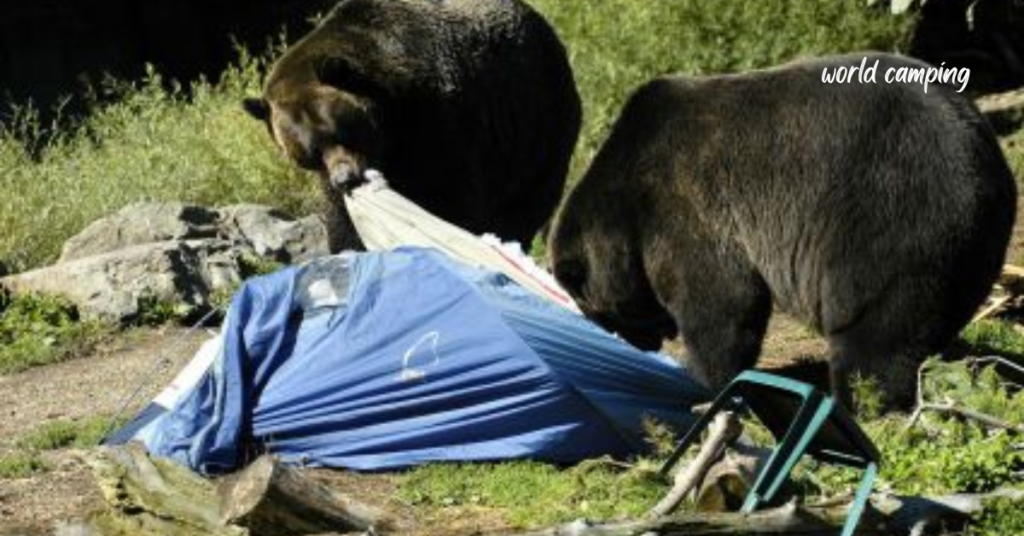

Camping brings you closer to nature, and this often means sharing the environment with wildlife. While most animals avoid human contact, encounters can occur, and knowing how to manage these situations is crucial for safety.
Common Wildlife Encounters
Encounters with wildlife are an inherent part of outdoor activities, and understanding how to safely navigate interactions with animals is essential for ensuring the well-being of both humans and wildlife. From bears and cougars to snakes and insects, various creatures inhabit outdoor environments and may pose risks to campers and hikers.
Bears are iconic inhabitants of many wilderness areas, and encounters can occur in regions where both black bears and grizzly bears are found. To minimize the risk of bear encounters, campers should practice proper food storage and waste disposal techniques, such as storing food in bear-resistant containers or hanging it from trees at a safe distance from the campsite. Additionally, making noise while hiking can help alert bears to your presence and reduce the likelihood of surprising them.
Cougars also known as mountain lions, cougars are elusive predators that inhabit remote and rugged terrain. While encounters with cougars are rare, campers should remain vigilant, especially in areas where cougar sightings have been reported. If you encounter a cougar, avoid running and instead stand your ground, make yourself appear larger, and slowly back away while maintaining eye contact. In the event of an attack, fight back aggressively using any available tools or objects.
Snakes are a common sight in many outdoor environments, with many species being harmless to humans. However, regions with venomous species like rattlesnakes require extra caution. Campers should watch their step when hiking in snake-prone areas and avoid reaching into areas where snakes may be hiding, such as rock crevices or dense vegetation. If bitten by a snake, seek medical attention immediately and avoid applying tourniquets or attempting to suck out venom.
Preventing Wildlife Encounters
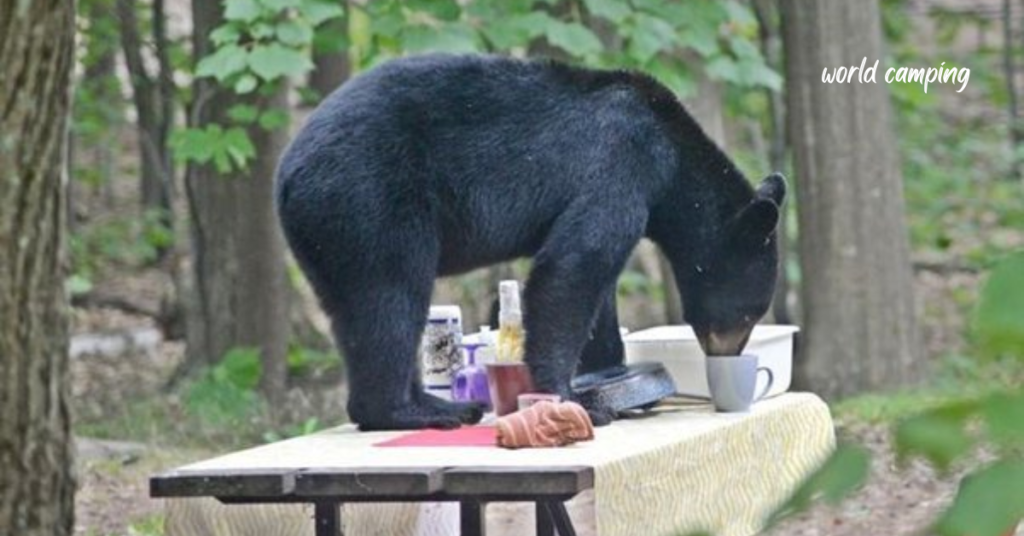

Preventing wildlife encounters is the most effective strategy for ensuring the safety of both humans and animals in outdoor environments. By taking proactive measures to minimize attractants and alerting animals to human presence, outdoor enthusiasts can reduce the likelihood of potentially dangerous interactions.
Proper food storage is essential for preventing wildlife from being attracted to campsites. Campers should use bear-resistant containers or hang food from trees at a safe distance from sleeping areas. Additionally, all trash and scented items should be stored securely to avoid attracting animals seeking food.
Keeping campsites clean and free of food scraps and waste helps minimize the likelihood of attracting wildlife. Campers should dispose of waste properly in designated trash receptacles and avoid leaving leftover food around the campsite. By maintaining a tidy campsite, campers can reduce the risk of unwanted animal visitors.
Strong smells from scented toiletries, perfumes, and cooking can attract wildlife to campsites. Campers should minimize the use of scented products and ensure that any scented items are stored securely to prevent animals from being drawn to the campsite.
Making noise while hiking is an effective way to alert wildlife, such as bears, of human presence and avoid surprising them. Campers should talk, clap, or sing loudly, especially in areas with dense vegetation or limited visibility where animals may be more difficult to spot.
Feeding wildlife or leaving food out can habituate animals to human presence and make them more aggressive in seeking out human food sources. Campers should never feed wildlife or leave food unattended, as this can create potentially dangerous situations for both humans and animals.
Conclusion & Recap
Camping in the wilderness is an enriching experience that allows you to connect deeply with nature. However, this connection comes with its set of risks and potential emergencies. Being prepared for such situations can mean the difference between a memorable adventure and a disaster.
Each scenario requires a calm, informed response and a proactive approach to safety. Medical emergencies necessitate immediate first aid and sometimes rapid evacuation. Weather-related crises, such as thunderstorms, flash floods, and extreme temperatures, require a keen awareness of the environment and swift, appropriate action to seek shelter and stay safe. Wildlife encounters highlight the importance of preventive measures, such as proper food storage and understanding animal behavior, while also knowing how to react if an encounter occurs.
FAQs
What should I do if I encounter a wild animal at my campsite?
Remain calm and don’t run. Slowly back away while making yourself appear larger. If the animal approaches, make loud noises and throw objects to scare it off.
How do I handle a medical emergency while camping?
Assess the situation and administer first aid if trained to do so. If the situation is severe, call emergency services immediately and provide clear details of your location and the nature of the emergency.
What steps should I take if a member of my camping group gets lost?
Stay calm and assess the situation. Begin searching nearby areas and call out the person’s name. If unsuccessful, notify park rangers or authorities, providing them with the last known location and any relevant details.
What should I do in the event of a sudden storm while camping?
Seek shelter immediately in a sturdy building or vehicle if available. If not, find low-lying areas away from tall trees and lie flat on the ground. Avoid open fields, high ground, and bodies of water.
How should I respond if my campfire gets out of control?
Quickly alert everyone in your group and attempt to contain the fire by smothering it with dirt, sand, or a fire blanket. If the fire spreads beyond control, evacuate the area immediately and call emergency services.




